RSV Season is Here: Take Measures to Prevent Your Newborn from Exposure
Darian Cooper 10/23/25
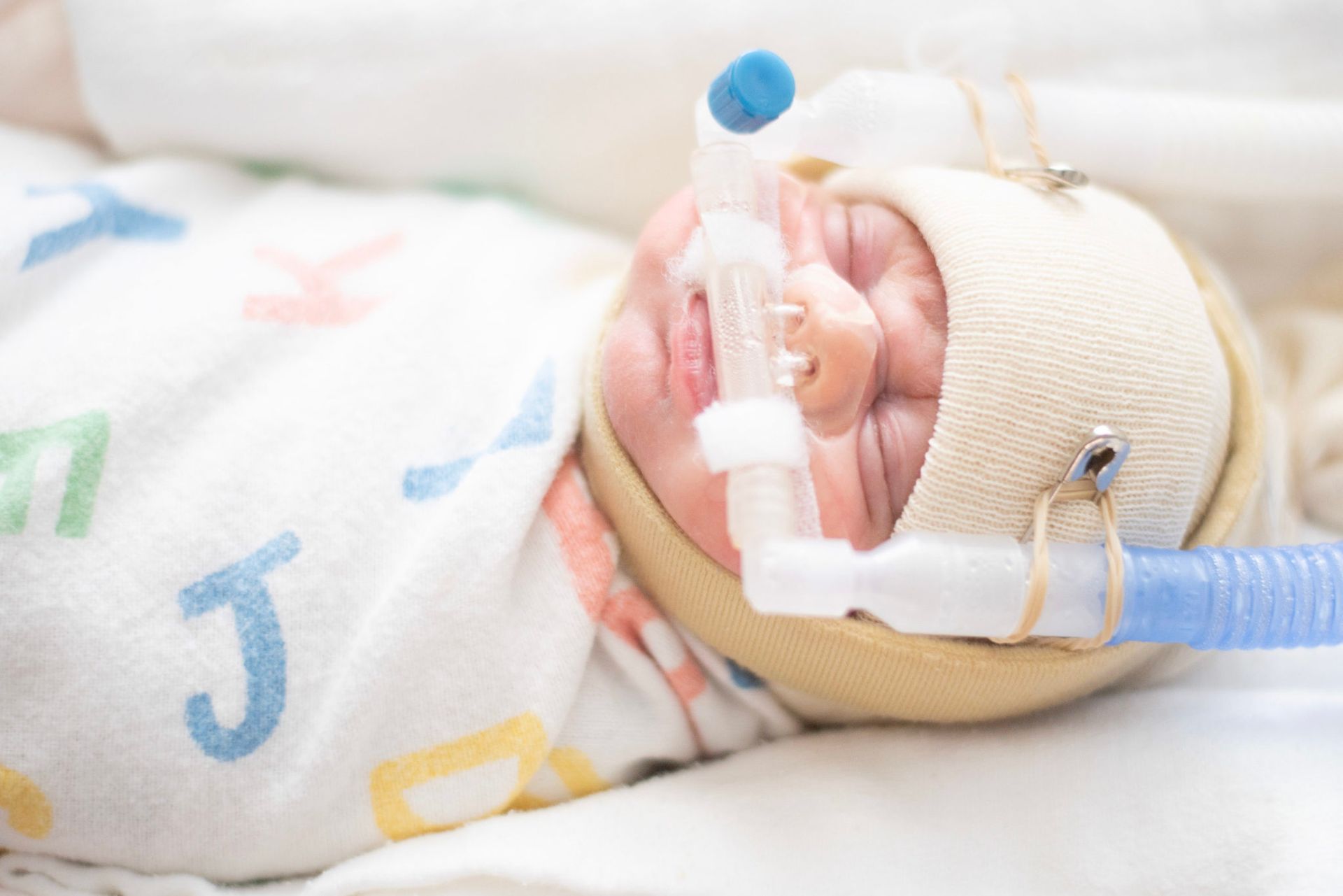
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that can affect people of all ages. RSV in newborns and babies can be particularly serious. RSV is a leading cause of respiratory tract infections in young children and can lead to bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
Here are some key points about RSV and newborns:
Transmission
The RSV virus is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also spread by touching a surface or object with the virus on it and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes.
Symptoms
RSV symptoms in newborns and babies can resemble those of a common cold, including cough, runny nose, and mild fever. However, it can progress to more severe respiratory symptoms, such as wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Risk Factors
Premature infants, infants with a weakened immune system, and those with certain heart or lung conditions are at a higher risk of severe RSV infection. Additionally, infants born during the RSV season (typically fall to spring) are more susceptible.
Prevention
There is no specific RSV treatment, so prevention is key. Strategies include administering the RSV vaccine, Nirsevimab specifically for infants younger than 8 months who are born during or entering RSV season 1. Practicing good hand hygiene, including frequent washing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and keeping the baby away from crowded places during the RSV season are also advised. In certain high-risk cases, a preventive medication called palivizumab2 may be recommended. Check with your childs health care provider.
Seeking Medical Attention
If a newborn or infant shows signs of respiratory distress, such as rapid breathing, difficulty feeding, or bluish skin color, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Hospitalization
Severe RSV infections may require hospitalization, especially if the baby is having difficulty breathing. In the hospital, supportive care such as oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids may be administered.
Parents and caregivers should be vigilant about the health of newborns, especially during the RSV season. If there are concerns about symptoms or potential exposure, it is advisable to contact a healthcare professional promptly. Always follow the guidance and recommendations of healthcare providers in managing and preventing respiratory infections in newborns.
More Resources:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
CDC – RSV in Infants and Young Children
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP):
AAP – Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Prevention
World Health Organization (WHO):
WHO – Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID):
NIAID – Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
1 https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/rsv/public/child.html accessed 1.17.24
2 https://www.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infections/clinical-guidance/interim-guidance-for-use-of-palivizumab-prophylaxis-to-prevent-hospitalization/ accessed 1.17.24




